Automating Solar Panel Installation: A LiDAR-based Perception System
Leveraging LiDAR point clouds to provide real-time, high-precision object detection for the robotic installation of solar panels in large-scale energy projects.
Motivation
Large-scale solar farms demand precise, efficient, and repeatable panel installation. Manual assembly is slow, costly, and error-prone. We build a real-time LiDAR perception system that delivers the accurate 3D parameters needed for robotic automation to scale installation while reducing cost.
Method Overview
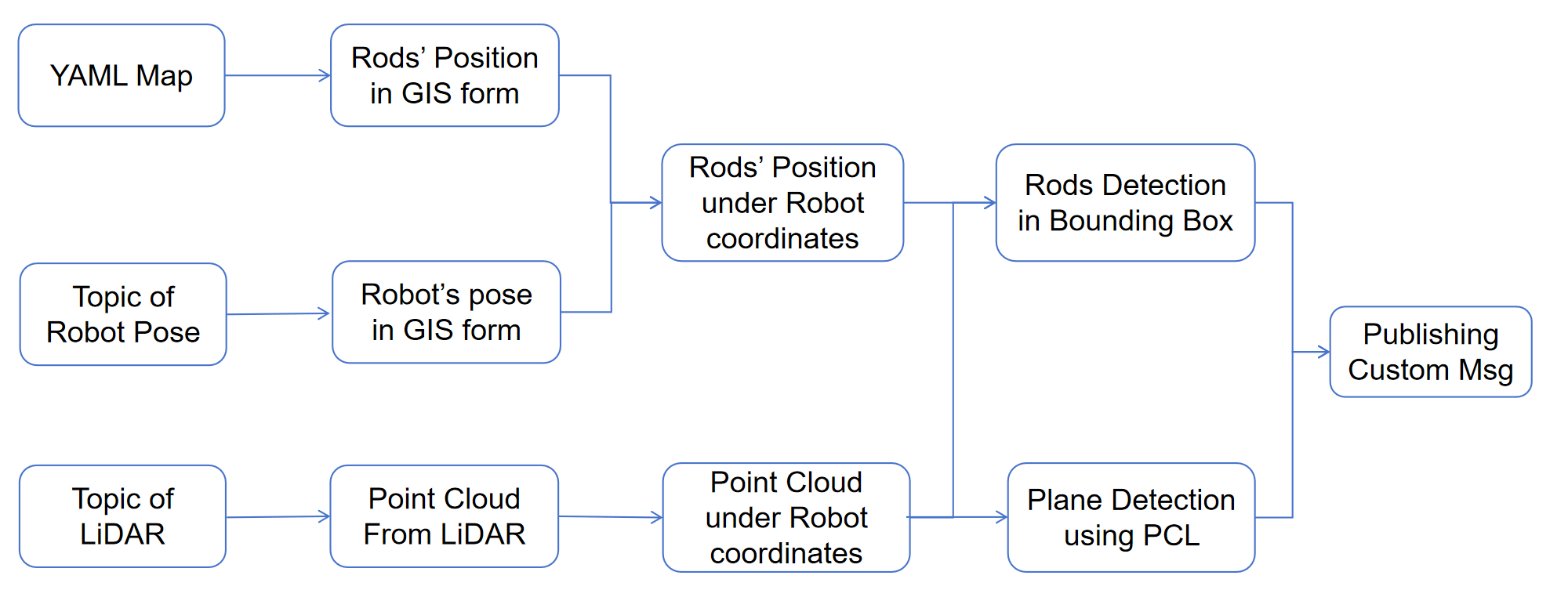
We process 3D LiDAR point clouds in real time to detect racks, posts, and panels, and to estimate their positions and orientations. These parameters (e.g., center coordinates, roll/pitch/yaw, post positions/angles) are published to the control system as actionable inputs for automated assembly.
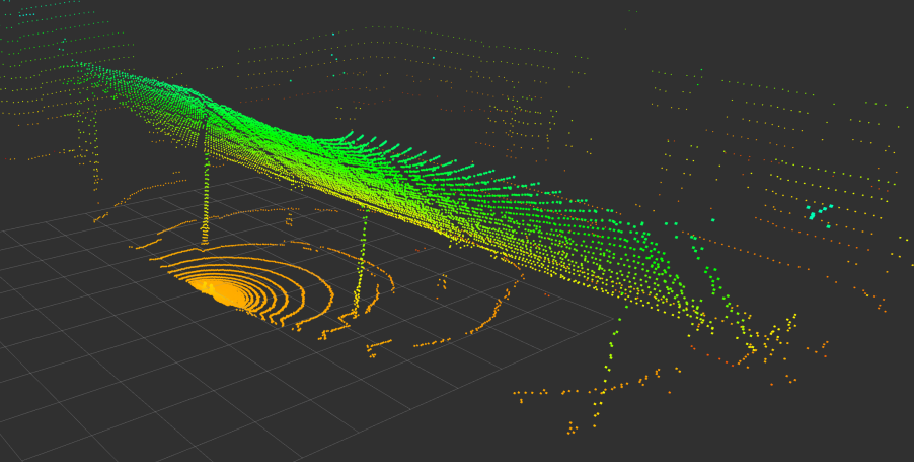
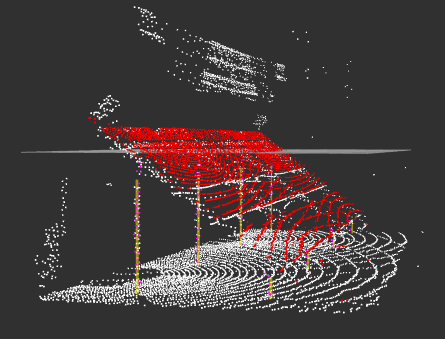
Perception Pipeline
Our ROS-based pipeline runs at 10 Hz for real-time operation:
- Sensor Fusion & Filtering: Fuse dual-LiDAR into a unified frame; denoise (statistical/passthrough) and downsample for speed.
- Plane & Line Segmentation: RANSAC plane models remove ground and fit panel surface (center + RPY); line models locate vertical posts using priors.
- Parameter Extraction & Publishing: Compute 3D positions and inclinations; publish custom ROS messages at 10 Hz with alerts for unsafe post angles.
System Architecture
Results
- Real-world Dataset: ROS bag from an active installation site with dual LiDARs (industrial partner).
- Real-time: End-to-end processing at 10 Hz.
- Detection: Accurate identification of panel and all 8 vertical posts.
- Pose Estimation: Example frame—panel inclination (36.7°, -2.9°); post position (-8.75, -1.36, -0.09) with near-zero inclination.
Tech Stack
- Robotics Framework: ROS (Robot Operating System)
- Point Cloud Processing: Point Cloud Library (PCL)
- Core Libraries: C++, Eigen
- Visualization: RViz
Project Impact
This project demonstrates a practical and effective solution for automating solar panel installation. By providing robots with accurate, real-time perception capabilities, our system enables a standardized installation process that improves efficiency, ensures positional and angular accuracy, and significantly reduces the costs associated with manual labor. It represents a key step toward a more streamlined and automated future for deploying solar energy infrastructure.
Project Team
- Developers: Dong Lingzheng, Jiajie Zhang (zhangjj2023@shanghaitech.edu.cn)
Related Resources
- Technical Report: Real-time Object Detection From LiDAR Point Clouds
This work contributes to the advancement of robotic automation in the renewable energy sector, showcasing the power of LiDAR perception in solving real-world industrial challenges.