AGLoc++: WiFi-Fused Global Localization and Monte Carlo Enhanced Tracking in Hierarchical Area Graph
Project Overview
AGLoc (link) proposes a robust indoor localization method using 3D LiDAR and hierarchical topo-semantic Area Graphs, achieving long-term stable performance in office environments by filtering dynamic clutter and matching architectural features (e.g., walls/doors), outperforming traditional SLAM approaches. This Project enhance the previous work in the following aspects:
- Port from ROS1 to ROS2 (Done)
- Implement WiFi-aided Kidnap Recovery (Done)
- Integrated with Nav2 stack by replacing AMCL (Done)
- indoor cross-level localizaiton (Done)
- Implement Odom-fused Monte Carlo Tracking (Doing)
- Re-localize when losing tracking (Doing)
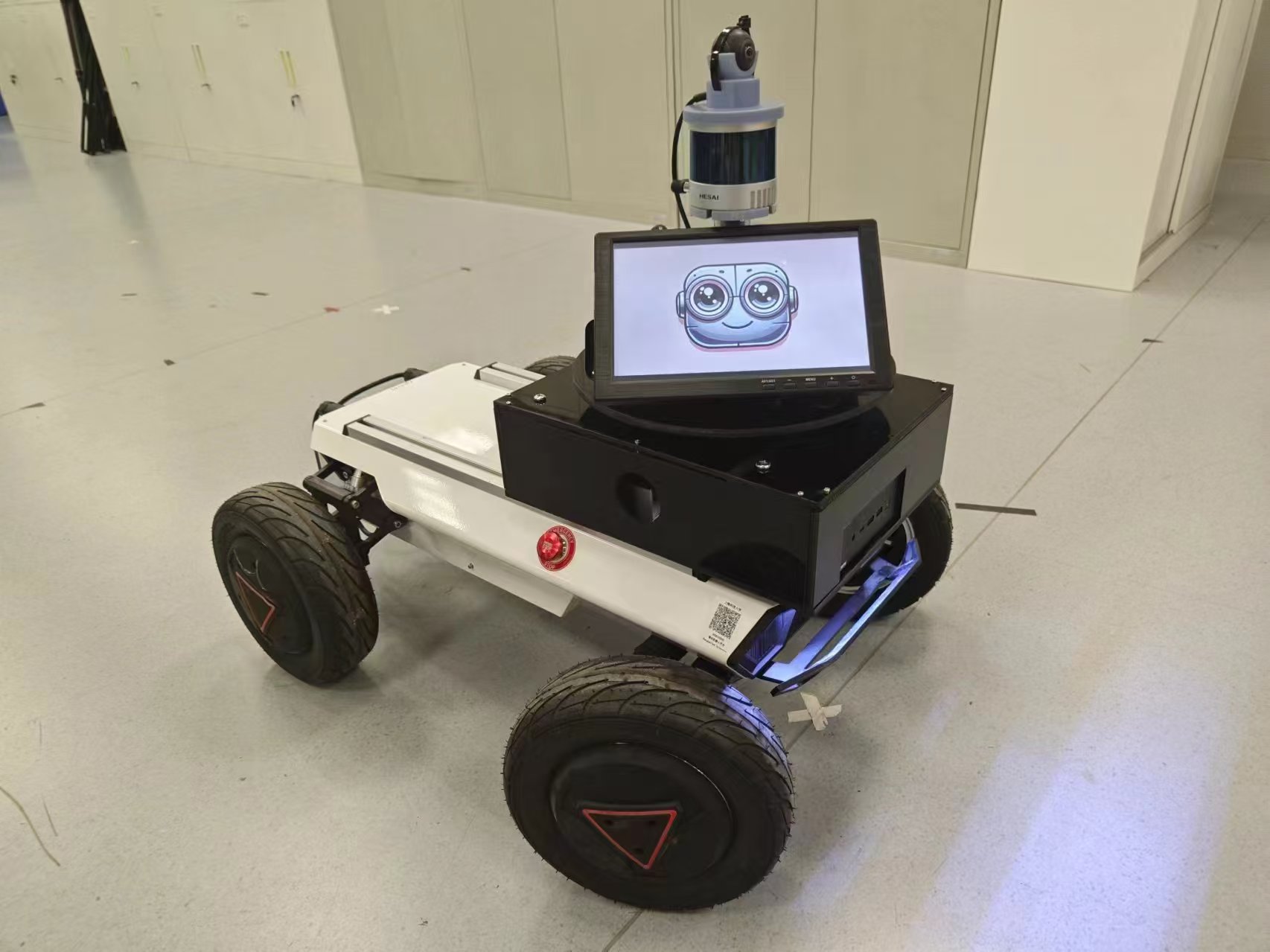

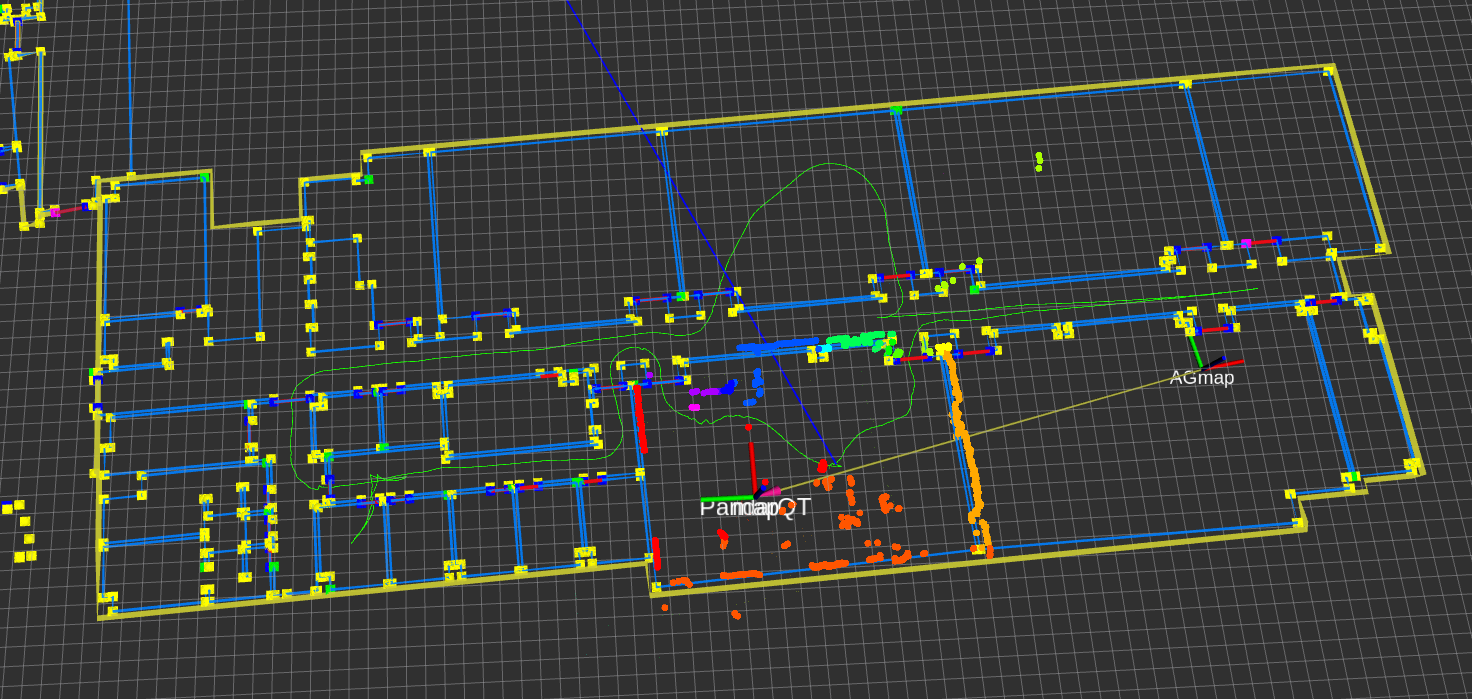
Key Technologies
- Long-term LiDAR localization framework based on the hierarchical Area Graph, enabling robust global and local localization in dynamic indoor environments.
- Clutter-adaptive subsampling to filter transient objects (e.g., furniture, pedestrians) from 3D LiDAR point clouds, preserving structural features (walls, doors).
- Hypothesis-scoring global localization to address the kidnapped robot problem: Candidate poses are sampled, ranked via a novel Area Graph match metric, and refined for reliability.
- Weighted point-to-line ICP with a clutter-aware weight function, ensuring pose tracking relies solely on lifelong architectural features (e.g., walls, passages).
- Corridorness-aware downsampling to optimize point cloud registration in corridor-dominated spaces, improving ICP accuracy.
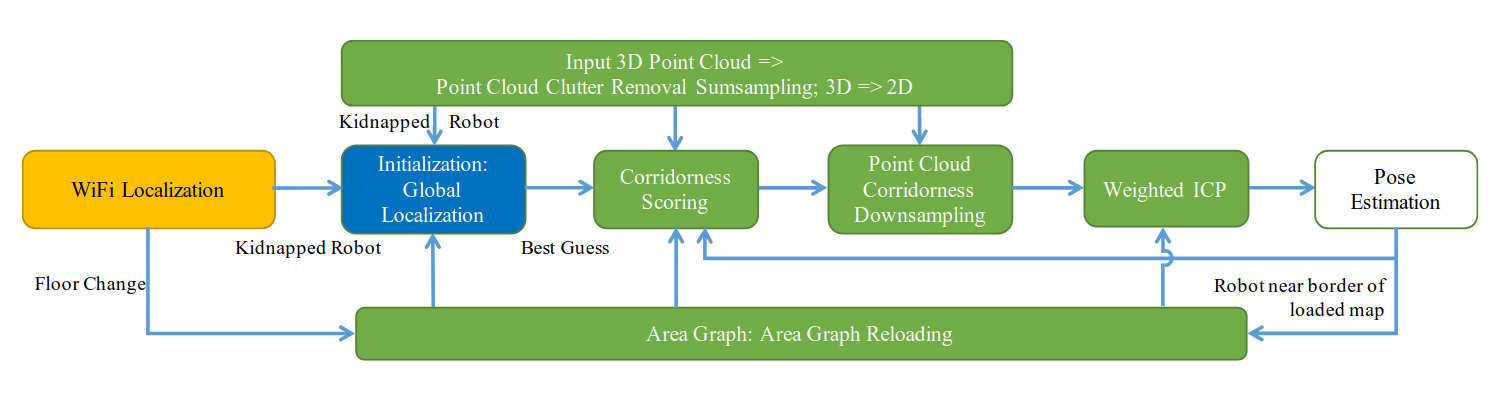
System Architecture
Future Work
Future development will focus on:
- Implement Odom-fused Monte Carlo Tracking
- Re-localize when losing tracking
- indoor cross-level re-localization
Project Team
- Current Work: Jiajie Zhang (zhangjj2023@shanghaitech.edu.cn)
- Previous Work: Fujing Xie (xiefj@shanghaitech.edu.cn)
